
EVERYTHING ABOUT AIRWAY BILL
The method of transporting goods by air has become increasingly popular and widely used. To utilize this service, a legally binding transportation document known as an Airway Bill (AWB) is required, provided by the carrier or their agent. If you are not familiar with this term, let’s explore the concept of an air waybill in the content below.
1. What is an Airway Bill (AWB)?
AWB, short for Airway Bill, is an air waybill – a document that accompanies goods shipped by international air transport. The AWB provides detailed information about the shipment and allows for tracking. This document has multiple copies so that each party involved in the shipment can retain a copy.
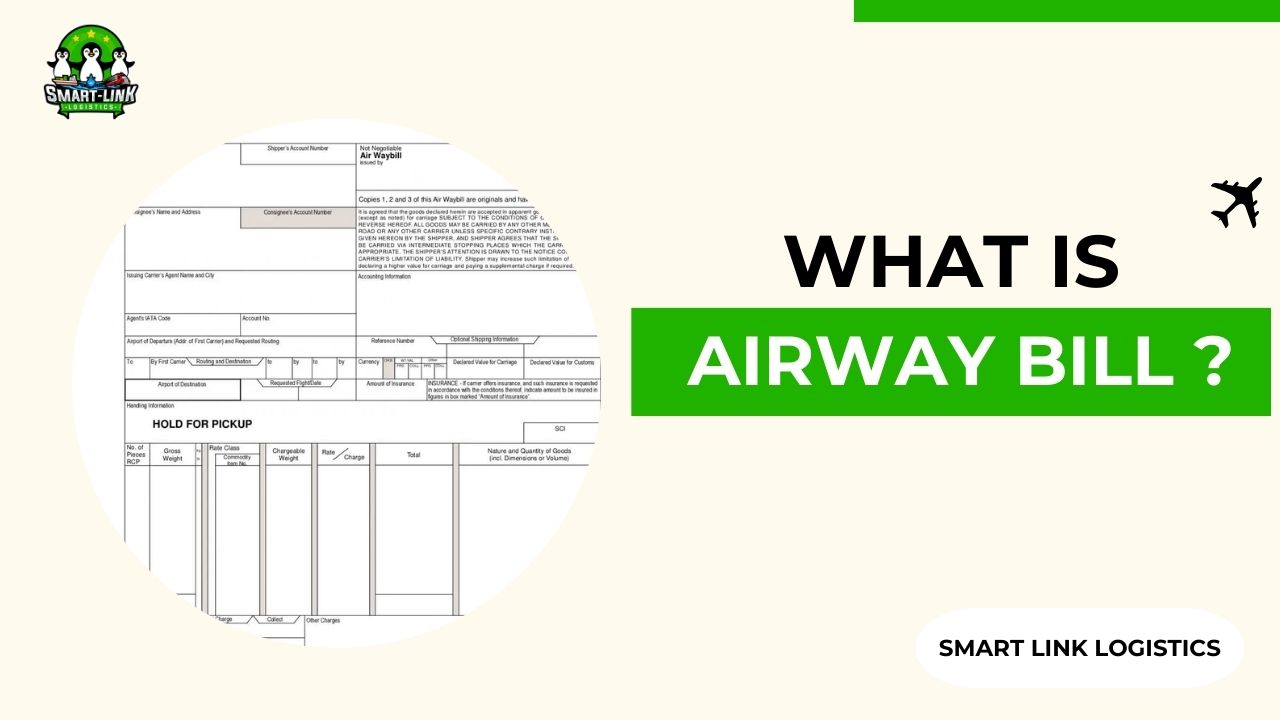
The AWB is similar to a sea waybill but is issued in a non-negotiable form. It contains detailed information about the shipment contents, the shipper, the consignee, terms and conditions, and other pertinent details. The AWB is a standard form distributed by the International Air Transport Association (IATA).
2. Functions of the airway bill
The AWB serves as a receipt for the goods by the airline and acts as a contract of carriage between the shipper and the carrier. This legal agreement becomes effective when both the shipper and the carrier (or their agent) sign the document.
The AWB includes information about the names and addresses of the shipper and consignee, the departure and destination airport codes, the declared value of the shipment for customs, the number of pieces, total weight, a description of the goods, and any special handling instructions (e.g., “perishable”).
Additionally, the AWB outlines the terms and conditions of the contract, such as liability limits and claims procedures, a description of the goods, and applicable charges.
3. Types of Airway Bill (AWB)
AWBs are categorized into two main types: MAWB and HAWB.
- MAWB (Master Airway Bill): The master airway bill, issued by the airline when receiving goods from a forwarding company to deliver them to the agreed destination.
- HAWB (House Airway Bill): The house airway bill, issued by the freight forwarder when receiving goods from the shipper and delivering them at the destination.
When a freight forwarder or consolidator is involved in the shipment, the forwarder receives the MAWB from the carrier or their agent as proof of receipt. The forwarder then issues a receipt for the shipper, known as the HAWB.
4. Contents of the Airway Bill
When filling out an AWB, it is crucial to check for accuracy to avoid errors. Here are some mandatory details on the AWB:
- Place and date of issuance
- Shipper’s name, full address, and signature
- Consignor’s name and address
- Place and date of receipt of the goods for transport
- Consignee’s name and full address
- Shipper and consignee’s reference numbers
- Description of the goods, packaging method, number of pieces, weight, dimensions: length, width, and height in centimeters or inches, and description of the goods including country of origin
- Product value
- Shipping costs
- Necessary information for customs procedures
- Additional information as per contract or specific express company regulations.
We hope this information helps you understand the concept of an Airway Bill and its importance in import-export and logistics! Here at our company, we provide you with services and solutions to help your goods reach the world with dedication and customer support. We take pride in being an established entity with over 13 years of experience in the transportation industry.
Hotline: + 84 903 354 157 to know more about our services

If you require assistance with international import and export of goods, please contact our team at Smartlink Logistics. We are available to provide you with professional guidance on our services and the necessary customs procedures.
SMART LINK: BEST SERVICE BEST YOU


































